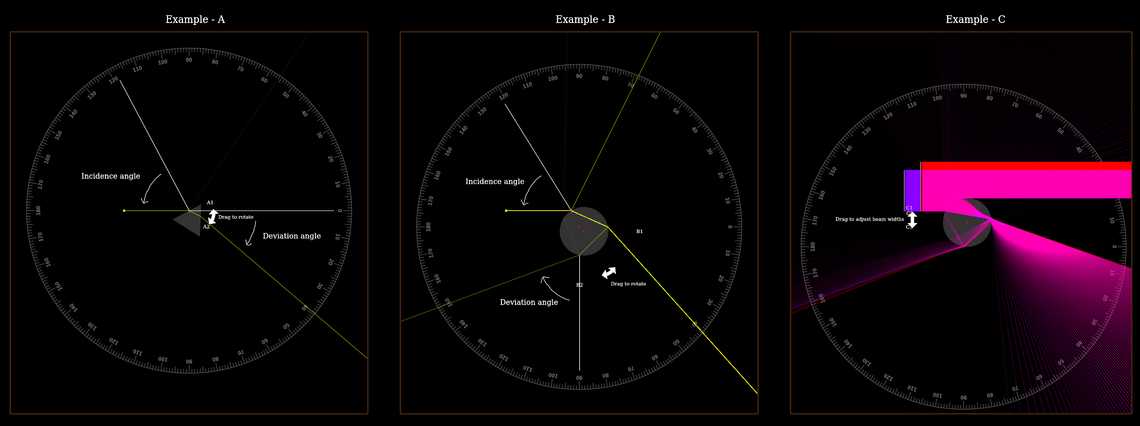
Contributor: Stas Fainer
The definition of the deviation angle of a ray hitting an optical element depends on the context - in the screenshot below you can see its definition for a triangular and a spherical prism. In the examples inside this simulation, the deviation angle as a function of the incidence angle of the ray entering the optical element, has a local minimum at a deviation angle which is called the "minimum deviation angle". This local minimum can explain optical phenomena such as rainbows and halos - due to this local minimum, the deviated rays accumulate at specific directions, creating "optical caustics" (as seen in example C inside the simulation) which we perceive as rainbows/halos.